Which Of The Following Services Can Be Measured And Monitored With Control Charts
Control Chart
Quality Glossary Definition: Command chart
Also called: Shewhart chart, statistical process command chart
The control chart is a graph used to study how a process changes over time. Data are plotted in fourth dimension society. A control chart always has a central line for the average, an upper line for the upper control limit, and a lower line for the lower control limit. These lines are determined from historical data. By comparing current information to these lines, you tin depict conclusions about whether the process variation is consequent (in control) or is unpredictable (out of control, affected by special causes of variation). This versatile information drove and assay tool can be used by a multifariousness of industries and is considered 1 of the 7 basic quality tools.
Control charts for variable data are used in pairs. The summit chart monitors the average, or the centering of the distribution of data from the process. The bottom chart monitors the range, or the width of the distribution. If your data were shots in target practice, the boilerplate is where the shots are clustering, and the range is how tightly they are clustered. Control charts for attribute data are used singly.
- When to use a control nautical chart
- Bones procedure
- Create a control chart
- Control chart resources
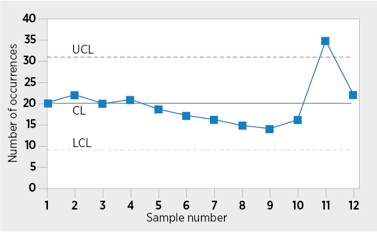
Control Nautical chart Example
When to Use a Control Nautical chart
- When controlling ongoing processes by finding and correcting problems as they occur
- When predicting the expected range of outcomes from a process
- When determining whether a process is stable (in statistical control)
- When analyzing patterns of procedure variation from special causes (non-routine events) or common causes (congenital into the process)
- When determining whether your quality improvement project should aim to forbid specific problems or to make key changes to the process
Basic Procedure
- Choose the appropriate control chart for your data.
- Determine the advisable time period for collecting and plotting data.
- Collect data, construct your chart and analyze the data.
- Look for "out-of-control signals" on the control chart. When ane is identified, mark it on the nautical chart and investigate the cause. Document how you investigated, what you learned, the crusade and how it was corrected.
Out-of-control signals
- A single point exterior the control limits. In Effigy one, point sixteen is in a higher place the UCL (upper command limit).
- Two out of three successive points are on the same side of the centerline and farther than two σ from it. In Effigy one, bespeak 4 sends that signal.
- 4 out of five successive points are on the same side of the centerline and farther than 1 σ from it. In Figure 1, point 11 sends that signal.
- A run of eight in a row are on the aforementioned side of the centerline. Or 10 out of 11, 12 out of 14, or 16 out of 20. In Figure i, point 21 is 8th in a row to a higher place the centerline.
- Obvious consistent or persistent patterns that suggest something unusual near your data and your process.
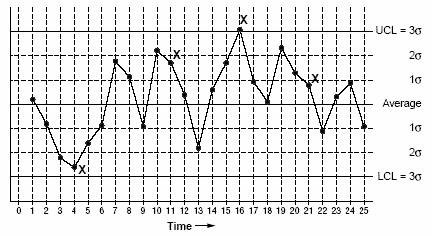
Effigy 1 Command Chart: Out-of-Control Signals
- Proceed to plot information every bit they are generated. As each new data bespeak is plotted, bank check for new out-of-command signals.
- When you outset a new command nautical chart, the procedure may exist out of control. If so, the command limits calculated from the beginning twenty points are conditional limits. When y'all have at least twenty sequential points from a menses when the process is operating in command, recalculate control limits.
Create a control chart
Encounter a sample control chart and create your own with the command nautical chart template (Excel).
Control Chart Resources
You can also search manufactures, case studies, and publications for control nautical chart resources.
Books
The Quality Toolbox
Innovative Control Charting
Improving Healthcare With Control Charts
Instance Studies
Using Command Charts In A Healthcare Setting (PDF) This teaching case study features characters, hospitals, and healthcare information that are all fictional. Upon utilize of the instance report in classrooms or organizations, readers should exist able to create a command chart and interpret its results, and identify situations that would exist appropriate for control chart analysis.
Quality Quandaries: Estimation Of Signals From Runs Rules In Shewhart Command Charts (Quality Technology) The example of Douwe Egberts, a Dutch tea and coffee manufacturer/distributor, demonstrates how run rules and a Shewhart control chart can be used as an effective statistical process control tool.
Articles
Spatial Control Charts For The Mean (Journal of Quality Engineering science) The properties of this command nautical chart for the means of a spatial process are explored with imitation data and the method is illustrated with an case using ultrasonic engineering to obtain nondestructive measurements of canteen thickness.
A Robust Standard Deviation Control Chart (Technometrics) Near robust estimators in the literature are robust against either lengthened disturbances or localized disturbances but not both. The authors suggest an intuitive algorithm that is robust against both types of disturbance and has better overall performance than existing estimators.
Videos
Control Chart
Excerpted from The Quality Toolbox , ASQ Quality Press.
Which Of The Following Services Can Be Measured And Monitored With Control Charts,
Source: https://asq.org/quality-resources/control-chart
Posted by: browningsubtromed87.blogspot.com


0 Response to "Which Of The Following Services Can Be Measured And Monitored With Control Charts"
Post a Comment